Respect for environmental protection measures and the rules of easy waste management is at the origin of the categorization of our garbage. The most common ones are plastic or metal waste and recyclable or organic waste. Green waste is one of the organic wastes of vegetable origin. So, without further ado, let’s dive into this blog and learn some of the things everyone needs to know about green waste.
Where does it come from?
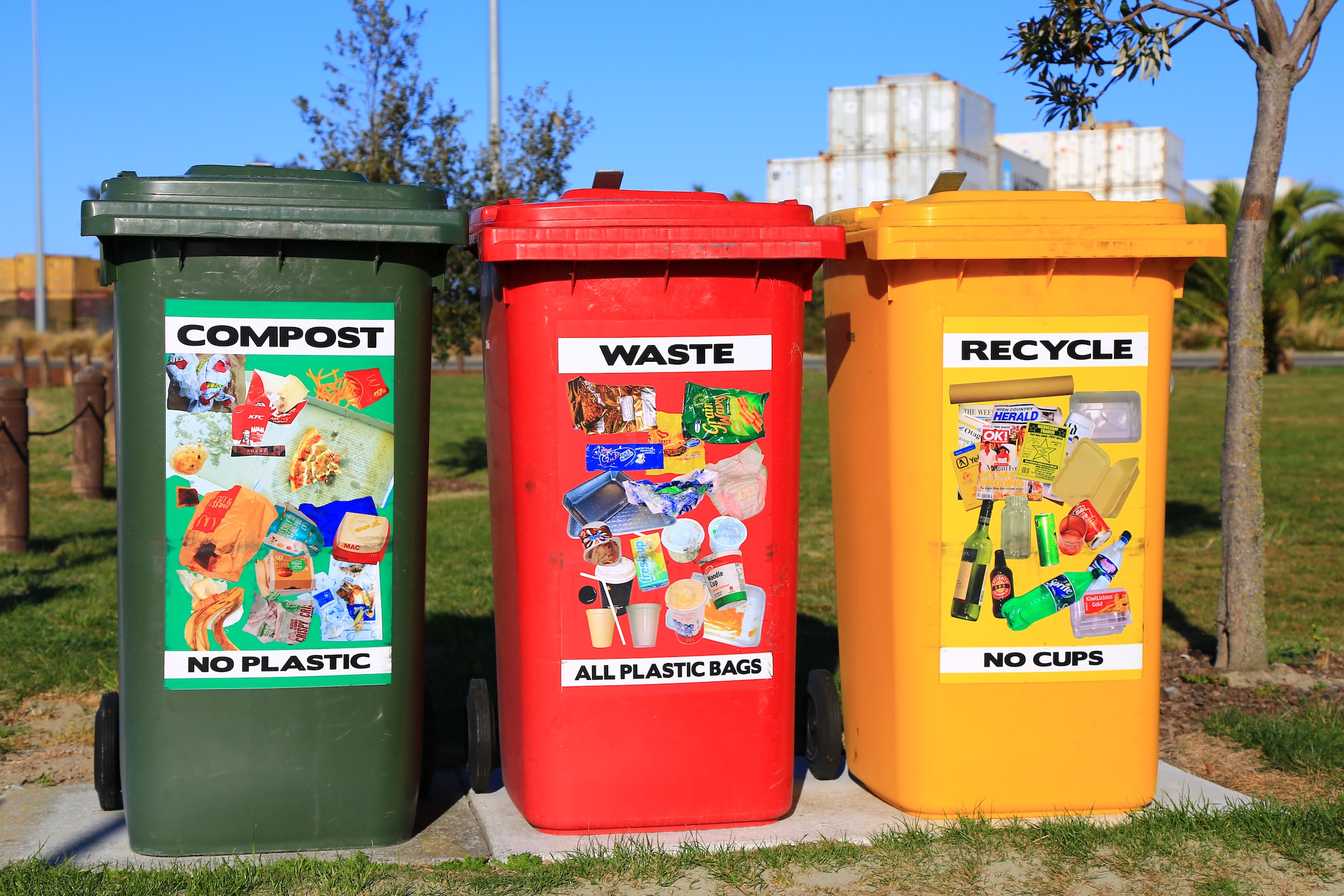

In general, green waste results from the pruning of plants during gardening and the maintenance of fruit trees or green spaces and parks carried out by households, private companies, or public authorities. These plant debris can also have a natural origin, such as the fall of dead leaves and stems. Therefore, it is made up of tree branches, dead leaves, grass, brush, and residues of plant and hedge pruning.
Why dispose of it?
Since vegetable waste is biodegradable, the inconvenience caused by its storage and the stench of its degradation causes a neighborhood disturbance. It is important to know that green waste is subject to certain regulations that must be respected:
-
- The storage of green waste whose volume is lower than 5 cubic meters is authorized, provided that it does not pollute water or the street. Beyond this threshold, municipal authorization is required.
-
- It is forbidden to throw them in the household garbage bins.
-
- Burning of vegetable waste is prohibited for individuals.
-
- The storage of bulky vegetal waste constitutes visual pollution. This aesthetic or visual damage done on a neighboring property is punishable by a fine
-
- For safety reasons, pruning work must be carried out by a company equipped with the appropriate materials.
How to get rid of it?
Generally, the disposal of green waste is under the responsibility of the municipality. The transportation of the waste is also the responsibility of the municipality. In practice, municipal technical services deposit dumpsters in each neighborhood. Thus, households, companies, or public communities are required to deposit their green waste there. In addition, in the absence of dumpsters, some municipalities offer to transport non-hazardous waste to the waste disposal center. This easy access has only two conditions:
-
- The cost of transporting the waste is at the expense of the depositor
-
- The depositor must bring proof of address issued by the commune in question.
What happens to vegetable waste?
It is taken to a dedicated area called the green waste area. Their destination varies according to the strategy of the commune concerned.
-
- Some of it is destined for recycling. For this purpose, green waste is sent directly to composting plants. There it is transformed into biogas, fuel, or fertilizer.
- Some municipalities enter into agreements with local farmers. This public-private partnership is called a co-composting agreement. The public authority deposits the sorted and shredded green waste on the partner’s farm through this partnership. This green waste is then processed and later used as fertilizer to promote agriculture.
- Wood and useful plant debris can also be purchased by companies specializing in the treatment and processing of wood. Properly dried, these wastes can be used later as firewood. Insofar as they are transformed, they will become recycled wood, ideal for the development of terraces and gardens, or will be used for modern carpentry activities.
Thanks to recycling, vegetable waste is transformed into essential elements of our daily life, such as firewood, fertilizer, garden furniture, and energy. The present facts only confirm the quote: “Nothing is lost, nothing is created, everything is transformed”.
Sound off in the comments section below, and tell us what you want to read next and if you want to read more about green waste.
