Introduction
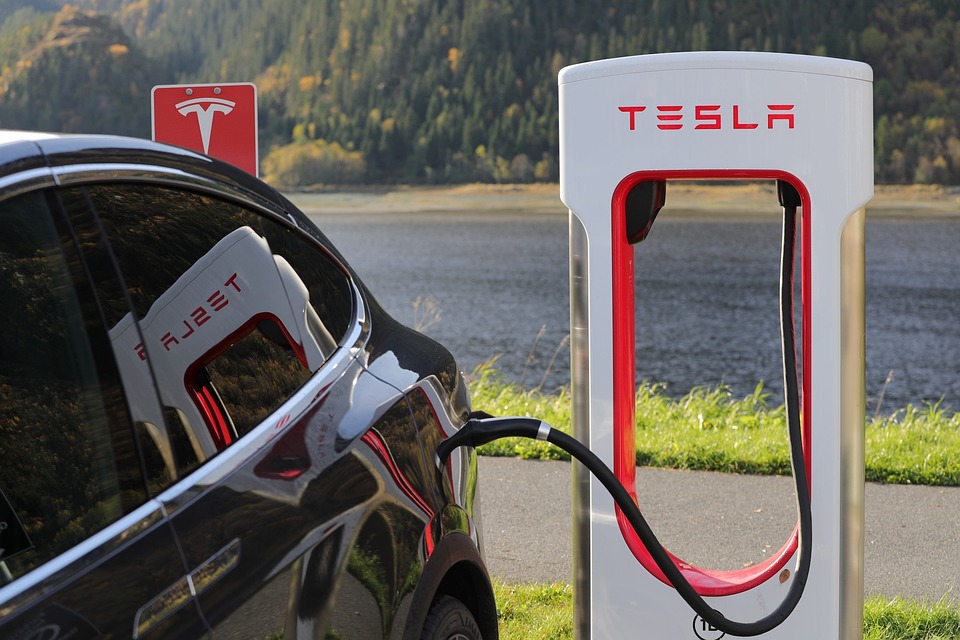
Electric cars, also known as electric vehicles (EVs), have become increasingly popular as a more sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars in recent years. As concerns over climate change and air pollution continue to grow, more people are turning to electric vehicles to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner environment. In this blog, we will explore how electric cars are more sustainable and eco-friendly than gas-powered cars and how they can benefit both the environment and the economy.
Reduced Emissions and Environmental Impact
One of the main reasons why electric cars are more sustainable than gas-powered cars is that they produce fewer emissions and have a lower environmental impact. Gas-powered vehicles emit harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and negatively affecting human health.
In contrast, electric cars do not emit any tailpipe emissions and are powered by clean energy sources such as wind, solar, or hydroelectric power. By driving an electric car, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and help mitigate climate change’s effects.
Lower Operating Costs and Maintenance
Another benefit of electric cars is that they have lower operating costs and maintenance requirements compared to gas-powered cars. Electric cars are more efficient in converting energy into motion, requiring less energy to travel the same distance as gas-powered car. This translates into lower fuel costs and a lower cost per mile for electric cars. In addition, electric vehicles have fewer moving parts than gas-powered cars, requiring less maintenance and a longer lifespan. This can save you money on repairs and maintenance over the car’s lifetime.

Improved Energy Security and Domestic
Jobs Electric cars can also improve energy security and create domestic jobs. Electric vehicles rely on electricity as their primary fuel source, which can be generated from various domestic sources, such as wind, solar, and hydropower. This reduces our dependence on foreign oil and improves our energy security. In addition, producing electric cars requires different skills and expertise than gas-powered cars, which can create new job opportunities in domestic manufacturing and supply chains.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Electric cars can also play a key role in integrating renewable energy sources into our energy system. As more renewable energy sources such as wind and solar are added to the grid, the variability of these sources can create challenges for grid operators. Electric cars can help to address this challenge by acting as mobile energy storage device. By charging electric cars during high renewable energy generation and discharging their batteries during high demand, electric cars can help balance the supply and demand of energy on the grid. This can improve the reliability and resiliency of our energy system and accelerate the transition to a clean energy future.
One of the challenges to the widespread adoption of electric cars is the lack of infrastructure for charging stations. However, this is changing rapidly as governments, and private companies invest in building more charging stations in public areas and private homes. In addition, advances in battery technology are making electric cars more efficient and cost-effective, making them more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
Electric cars are a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to gas-powered cars. They produce fewer emissions, have lower operating costs and maintenance requirements, and can contribute to improved energy security and the creation of domestic jobs. In addition, electric cars can play a key role in integrating renewable energy sources into our energy system, improving the reliability and resiliency of our energy system and accelerating the transition to a clean energy future. As more people adopt electric cars, we can create a cleaner, more sustainable, and more prosperous future for ourselves and for future generations.